3.3 VLANs
Using traditional LAN segmentation, all the segments will be in the same broadcast domain. This effectively, reduces the efficiency of the network. A traditional LAN segmentation is shown below.
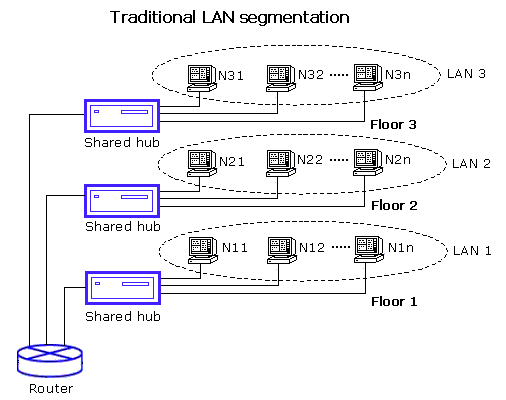
Figure 1: Traditional LAN Segmentation
VLANs: Using VLANs, the broadcast domain gets divided into the number of VLANs. If there are three VLANs, as shown in the figure, the broadcast domain will be split into three.
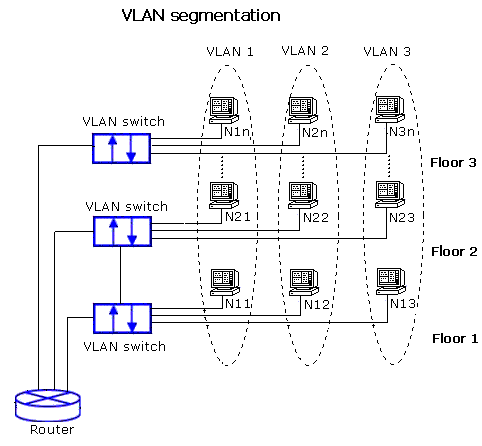
Figure 2: Segmentation using VLANs
Logical View: Given below is the logical view of segmentation using VLANs. Note that a router is required to route traffic between VLANs, and each VLAN is in different broadcast domain.
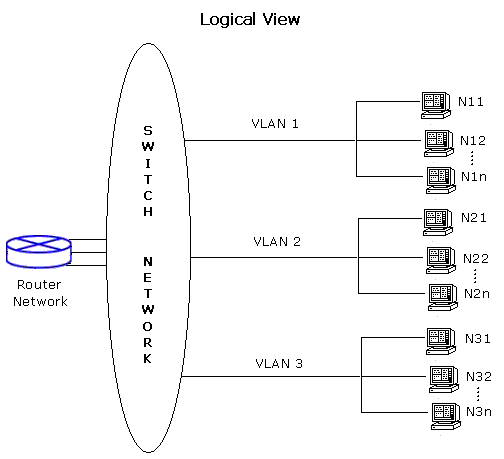
Only a single router is shown for simplicity. One or more routers may be used for routing interVLAN traffic.
With VLAN, its logical topology is independent of the physical topology. Each computer can be assigned a VLAN identification number (ID), and computers with the same VLAN ID can communicate freely as if they were on the same physical segment. The communications between VLANs is secure, because the packets meant for one VLAN will not be forwarded to other VLANs.
Disclaimer: Simulationexams.com is not affiliated with any certification vendor, and Sim-Ex™ Practice Exams are written independently by SimulationExams.com and not affiliated or authorized by respective certification providers. Sim-Ex™ is a trade mark of SimulationExams.com or entity representing Simulationexams.com.A+™,Network+™,Security+™,Server+™ are trademark of CompTIA® organization.