3.2 Firewalls
A firewall is a device (sometimes it could be a system) that prevents un-authorized access to a network from external sources. For example, any network that is connected directly to the Internet need some kind of firewall to protect the entire network from potential intrusions from the Internet.
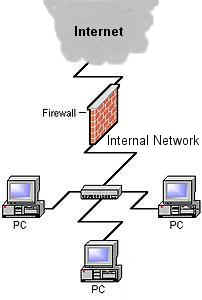
A "Firewall" may be implemented using one or more of the following technologies:
| Sl. No. | Firewall technology | OSI layer at which the firewall operates |
| 1. | Proxy service | Layer 7 |
| 2. | Packet Filtering | Layers 3 and 4 |
| 3. | Stateful inspection | Layers 2,3, and 4 |
Proxy servers: Proxy servers hides network resources behind itself. For example, by using Proxy Server, the internal IP addresses of a Corporate network can be made invisible to the external world. It is usually a software program, that resides as an application on top of the Operating System. A Proxy Server may work at several layers of OSI model, validating the data at each layer.
Network Address Translator (NAT): Network Address Translation enables an internal network to use one set of IP addresses for internal traffic and a second set of addresses for external traffic. A NAT box located where the local network interfaces with the external network.
NAT serves three main purposes:
There are two types of NAT widely used:
Static NAT: In a Static NAT, a private IP address is mapped to a fixed public IP address. The public address is always the same IP address for a given internal private IP address. The advantage of having a fixed mapping of private IP to public IP is that the internal resources such as web server can be reached from external network. The main disadvantage is that it still takes one precious IP address from the public Internet.
Dynamic NAT: Dynamic NAT maps a private IP address to a public IP address that is dynamically selected from a pool of one or more public IP addresses. The main advantages of dynamic NAT include the following:
One of the main disadvantages is that if you need to locate a server on the internal network, such as an e-mail server, that has to be accessed from the public Internet, then you can not use dynamic NAT. The internal email server has to be assigned with a static mapping of IP address.
Packet Filtering:Packet Filtering is the ability of a router or a firewall to discard packets that don't meet certain criteria. A packet filtering router should be able to filter IP packets based on the following four fields:
Filtering is used to:
Packet filtering is usually employed by routers, and faster than Proxy servers that operate at higher layers. The main disadvantage of packet filters is that they operate at layer 3/4 of OSI model, and do not have the capability to analyze data or the traffic. As a result, it is possible for malicious applications to enter a protected network.
Access Control List (ACLs): ACL is similar to packet filtering.
The Demilitarized Zone (DMZ): DMZ is used by most of the firewalls, which is a network segment that is neither public nor local, but halfway between. A standard DMZ setup has three network cards in the firewall computer. The first goes the Internet, the second goes to the network segment and the third connects to the intranet.
Disclaimer: Simulationexams.com is not affiliated with any certification vendor, and Sim-Ex™ Practice Exams are written independently by SimulationExams.com and not affiliated or authorized by respective certification providers. Sim-Ex™ is a trade mark of SimulationExams.com or entity representing Simulationexams.com.A+™,Network+™,Security+™,Server+™ are trademark of CompTIA® organization.