The display devices used commonly can be classified as below:
Cathode Ray Tube (CRT):
CRT display is the most commonly used form of visual displays, through it is getting gradually replaced with LCD and Plasma displays.

A computer monitor using CRT display.
In a CRT, an electron beam sweeps the display screen horizontally, one line at a time, gradually down the screen. A synchronization (sync) signal brings the beam back to the top row of the display. This type of scanning (line-by-line) is known as raster scan.
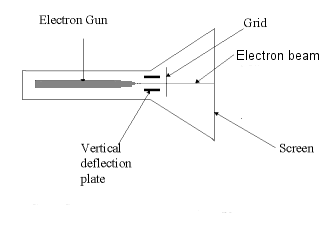
Figure: CRT cross sectional diagram showing important components of a CRT
There are two types of cathode ray displays. One is non-interlaced, and the other is interlaced. Normally, all the displays are interlaced to reduce flicker.
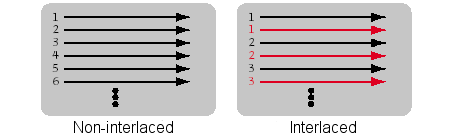
As shown in the figure, for non-interlaced display, the scanning is done continuously from top to bottom. For non-interlaced display, alternate rows are scanned.
A black and white monitor contains only one electron gun, whereas a color display monitor will have three electron guns, each of which represent red, green, and blue.
The horizontal and vertical deflection takes place by applying appropriate voltages to the horizontal, and vertical deflection plates. Usually, the screen is refreshed between 60-100 times per second.
The grid shown in the figure controls the speed with with the electrons hit the screen. If a positive voltage is applied to the screen grid, because of which the electrons are accelerated and hit the screen, making the screen brighter. If a negative voltage is applied to the grip, the electrons are decelerated and the screen will not glow. The microscopic control of electron beam flow, produces images on the screen.
One basic unit of measurement is "pixel". A pixel is the smallest area in a graphics display that can be manipulated.
Given below are the commonly used screen resolutions:
| Display Type | Number of pixels |
| Video Graphics Array (VGA) | 640 * 480 pixels |
| Super Video Graphics Array(SVGA) | 800 * 600 pixels |
| eXtended Graphics Array (XGA) | 1024 * 768 pixels |
| Super eXtended graphics Array (SXGA) | 1280 * 1024 pixels |
Screen resolution is always stated as the horizontal number of pixels by the vertical number of pixels. A screen displaying 800 x 600 pixels has 600 rows, each 800 pixels wide.
Graphics Cards: The graphics card resides in the CPU box, and drives the video display. A typical graphics card is shown below:
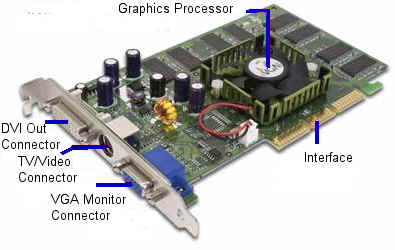
The graphics card shown includes DVI connector, TV/Video connector, and a VGA connector. The card has an on-board graphics processor with cooling fan. Usually, for graphic intensive applications, you need a higher end graphic adapter card. For normal desktop usage, a video adapter will be sufficient.
Download practice tests:
Download Sim-Ex™ Practice Exams for A+ Core 1
Download Sim-Ex™ Practice Exams for A+ Core 2
Related practice tests:
Sim-Ex™ Practice Exams for Network+
Sim-Ex™ Practice Exams for Server+
Sim-Ex™ Practice Exams for Security+
Disclaimer: Simulationexams.com is not affiliated with any certification vendor, and Sim-Ex™ Practice Exams are written independently by SimulationExams.com and not affiliated or authorized by respective certification providers. Sim-Ex™ is a trade mark of SimulationExams.com or entity representing Simulationexams.com.A+™,Network+™,Security+™,Server+™ are trademark of CompTIA® organization.