1.2 Physical Topologies:
The term "Physical topology" is used to explain the broad layout of the network cables and workstations, and the location of all network components. It is also indicative of how the information or data flows within the network. The five most common topologies are:
Bus Topology: In this topology all the computers are attached to a single continuous cable. The cable is typically a co-axial one, and terminated at both the ends. The cable termination at the ends ensures that the signals are not reflected after reaching the end of the cable. The computers are attached to the cable using wire taps. Using Bus Topology, the information signals are available at every individual workstation. However, the individual work stations discard information that is not meant for them.
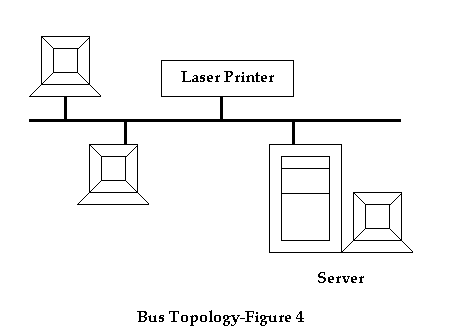
Bus topology network is simple to install, inexpensive, and easy to maintain. However, there are several disadvantages of using this topology:
1. Any cut in the cable will result in severe communication disruption, and need to be fixed on priority.
2. It is difficult to affect server, and workstation moves.
Star Topology: In a star topology each computer is connected to a centrally placed Hub or a Switch by a separate cable. A typical star topology network is shown below.
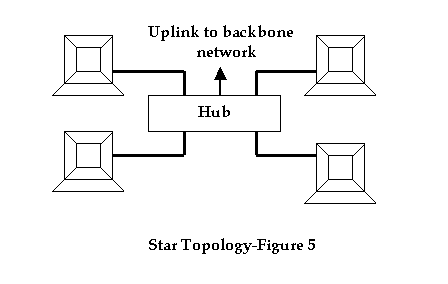
Star Topology is the most widely used network topology, and has the following advantages:
Ring Topology: In the ring topology each computer is connected directly to two other computers (one in the up-stream, and another in the down-stream) in the network. A typical network using Ring Topology is shown in the figure below:
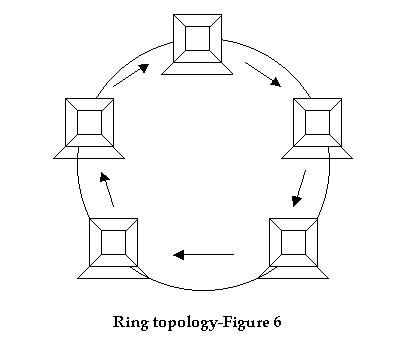
The main advantages of Ring Topology include high bandwidth capacity, fault location identification, and ability to cover relatively larger distances. The main disadvantage is that a single cable fault may bring down the network.
Mesh Topology: In Mesh topology, a path exists from each node to one or more nodes in the network. In a Full Mesh, every node will have a connection to every other node in the network. A typical diagram shown full mesh connections among five nodes (or hosts) is shown in the figure below:
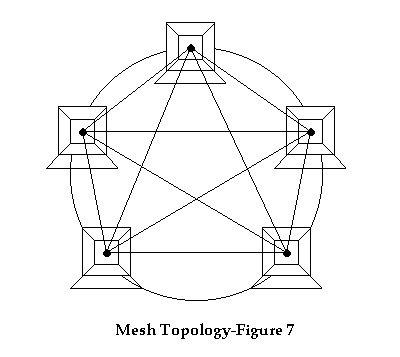
The main advantage is redundancy. If one connection fails, a node can communicate over another network connection. The chief disadvantages are cost and complexity of the topology.
Among the topologies discussed, Star Topology is the most widely used. Ring Topology is used when you need to connect several smaller networks (say, using Star Topology) using high bandwidth backbone.
Disclaimer: Simulationexams.com is not affiliated with any certification vendor, and Sim-Ex™ Practice Exams are written independently by SimulationExams.com and not affiliated or authorized by respective certification providers. Sim-Ex™ is a trade mark of SimulationExams.com or entity representing Simulationexams.com.A+™,Network+™,Security+™,Server+™ are trademark of CompTIA® organization.