2.0 Laptop and Portable Devices
2.2 Install, configure, optimize and upgrade laptops and portable devices
Identify the features of BIOS-ACPI
ACPI is an acronym for Advanced Configuration and Power Interface, a power management specification developed by Intel, Microsoft, and Toshiba. ACPI support is built into Windows 98 and later operating systems. ACPI is designed to allow the operating system to control the amount of power provided to each device or peripheral attached to the computer system. This provides an efficient power management and makes it possible for the operating system to turn off selected devices, such as a monitor or CD-ROM drive, when they are not in use.
Windows Server 2003, Windows XP, and Windows 2000 require that an ACPI BIOS be dated January 1, 1999 or later. However, if one of these Windows versions determines that such a BIOS is known to exhibit ACPI problems, the loader disables ACPI and instead uses Advanced Power Management (APM). Beginning with Windows Vista, the operating system only supports a computer with an ACPI-compliant BIOS that is dated January 1, 1999 or later.
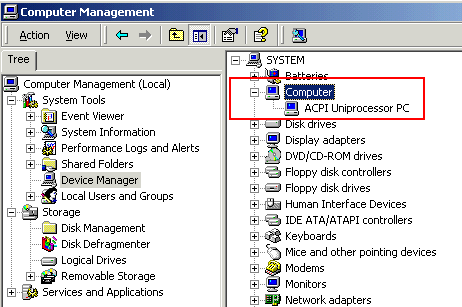
Device Manager shows whether an individual computer supports ACPI.
Identify the difference between suspend, hibernate and standby
Hibernate and Standby are two different sleep modes available in Windows XP. Hibernate saves an image of your desktop, including all open windows and files. Then it powers down your computer just as if you had turned it off. When the computer is turned on later, all windows screens and files are open just as you left them.
Standby reduces the power consumption significantly. When you select Standby, the power to your display, hard drive, and peripheral devices is turned off. However, the power to the computer's memory (RAM), and other essential elements of the motherboard is maintained so your open files stay open. Standby is typically recommended when you are away from your computer for a few minutes to less than a couple of hours. Standby mode doesn't save your work to the hard disk. If you are going to be away for sever hours, use hibernate or shut down the computer.
Configuring Power Settings
Using Power Options in Control Panel, you can adjust any power management option that your computer's unique hardware configuration supports. Because these options may vary widely from computer to computer, the options described may differ from what you see. Power Options automatically detects what is available on your computer and shows you only the options that you can control. To configure your power settings:
1. Click Start, click Control Panel, click Performance and Maintenance, and then click Power Options.
2. Or, if you see the battery indicator on your task bar, right-click it and then click Adjust Power Properties. The Power Options Properties dialog box opens, as shown in Figure below:
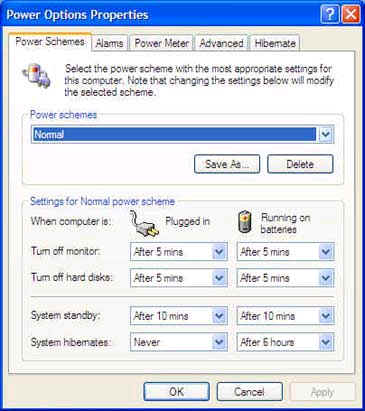
In the Power Options dialog box, you set options for a power scheme.
Disclaimer: Simulationexams.com is not affiliated with any certification vendor, and Sim-Ex™ Practice Exams are written independently by SimulationExams.com and not affiliated or authorized by respective certification providers. Sim-Ex™ is a trade mark of SimulationExams.com or entity representing Simulationexams.com.A+™ is a trademark of CompTIA® organization.